In a swift operation that underscores Russia’s growing crackdown on domestic cyber threats, the Ministry of Internal Affairs (MВД) has arrested a group of young IT specialists accused of creating and distributing the Meduza Infostealer malware.
This credential-harvesting tool, which has been circulating on underground forums since mid-2023, specializes in siphoning login details, cryptocurrency wallet data, and other sensitive information from infected Windows systems.
The arrests, conducted in Moscow and the surrounding region with support from Rosgvardia forces, come after the group allegedly used their own malware to breach a government institution in Astrakhan earlier this year.
The Bust: How Russian Law Enforcement Took Down the Meduza Crew
The operation targeted a tight-knit group of developers who had been active for approximately two years, starting around 2023. According to official statements from MВД spokesperson Irina Volk, the suspects were detained following an investigation into unauthorized access incidents. In May 2025, the group reportedly deployed Meduza to infiltrate an Astrakhan-based institution, copying protected official data to their controlled servers.This breach served as a key trigger for the probe, leading to coordinated raids where authorities seized computer equipment, mobile devices, bank cards, and other evidence.
A criminal case has been opened under Part 2 of Article 273 of the Russian Criminal Code, which covers the creation, use, and distribution of malicious software. Investigators also uncovered that the group had developed additional malware aimed at disabling security protections and building botnets for large-scale DDoS attacks.
While specific names haven’t been released, the detainees are described as young IT experts, highlighting how accessible malware development has become in underground circles. Preventive measures, including possible house arrest or detention, have been applied to at least three individuals as the investigation continues to identify all accomplices and related crimes.This isn’t the first time Russian authorities have targeted homegrown cyber threats, but the focus on an infostealer like Meduza, often sold as a subscription service on dark web forums, suggests a broader effort to curb tools that fuel global data breaches.

Meduza Infostealer: Features and Capabilities
Meduza Infostealer, emerged in June 2023 as a Windows-targeted trojan marketed on cybercrime forums and Telegram channels. Priced from $199 for a one-month subscription to $1,199 for lifetime access, it positions itself as a superior alternative to established stealers like Redline, Raccoon, and Vidar. The malware boasts a user-friendly GUI for attackers, allowing easy customization and log management.
Key features include:
- Browser Data Theft: Supports over 100 browsers, including Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Opera, Brave, and Yandex. It extracts login credentials, cookies, history, bookmarks, autofill data, and local storage.
- Cryptocurrency Focus: Targets more than 100 wallets, from browser extensions like MetaMask, Trust Wallet, and Binance Chain to desktop apps such as Exodus, Coinomi, and Bitcoin Core. It grabs wallet files, seeds, and registry data.
- Password and 2FA Extraction: Hits password managers like 1Password, LastPass, Bitwarden, Dashlane, and KeePassXC, plus 2FA extensions such as Authenticator and Authy.
- App-Specific Grabs: Steals from messaging apps (Telegram, Discord), gaming platforms (Steam), VPNs (OpenVPN), email clients (Outlook), and even miner-related data.
- System Recon: Collects hardware details (CPU, GPU, RAM), IP address, timezone, screenshots, and installed software lists for victim profiling.
- The stealer operates stealthily: Upon execution, it checks the victim’s geolocation and aborts if they’re in excluded CIS countries (e.g., Russia, Kazakhstan, Belarus) to avoid local heat.
* This list was made available by the research “Meduza Stealer Malware: What Is It & How Does It Work?” by uptycs
Insights from the Underground: Developer Perspectives
Prior to the arrests, the Meduza team was vocal on forums, positioning their tool as a “stable and ideal” stealer with ongoing updates.
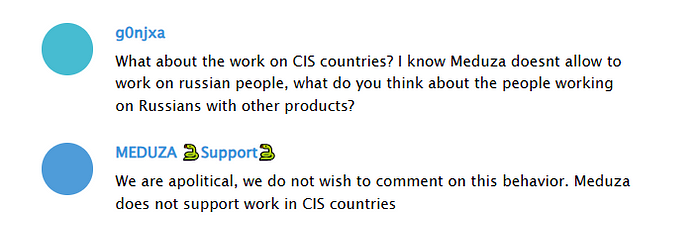
In developer communications leaked through threat intel, they emphasized non-ransomware focus, AV evasion, and custom features like file grabbers – echoing sentiments from similar infostealer creators. From a brief interview conducted with the Meduza developer, as part of the “Approaching Stealers Devs” series by g0njxa, key insights reveal the project’s approach to the market.
The developer declined to disclose the number of active clients, aligning with a common practice among stealer operators for operational security. On the topic of targeting CIS countries, Meduza explicitly prohibits it, aborting infections in regions like Russia to avoid attracting local law enforcement, ironically, the very authorities that now appear to have caught up with them.
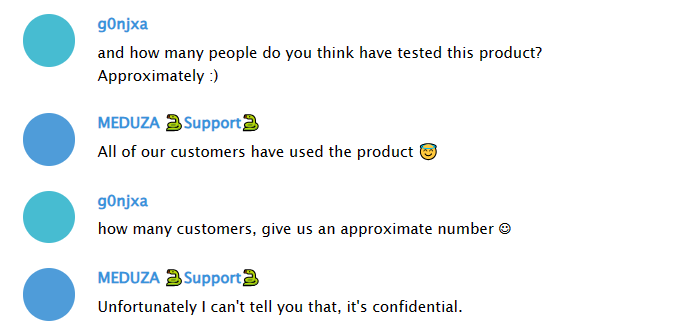
Regarding market stability, the developer commented that the infostealer market is stable, though the interviewer noted this view might be more reflective of Meduza’s own position rather than the volatile broader ecosystem, where bans and disruptions are frequent.
The developer also highlighted efforts to carve out a niche, stating that Meduza is “trying hard to get a spot in the market,” with the interviewer opining that these efforts were not in vain given its growth prior to the bust.
This arrest may deter future devs, but the code could live on through forks or resales.
To learn more about how Hudson Rock protects companies from imminent intrusions caused by info-stealer infections of employees, partners, and users, as well as how we enrich existing cybersecurity solutions with our cybercrime intelligence API, please schedule a call with us, here: https://www.hudsonrock.com/schedule-demo
We also provide access to various free cybercrime intelligence tools that you can find here: www.hudsonrock.com/free-tools
Thanks for reading, Rock Hudson Rock!
Follow us on LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/hudson-rock
Follow us on Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/RockHudsonRock