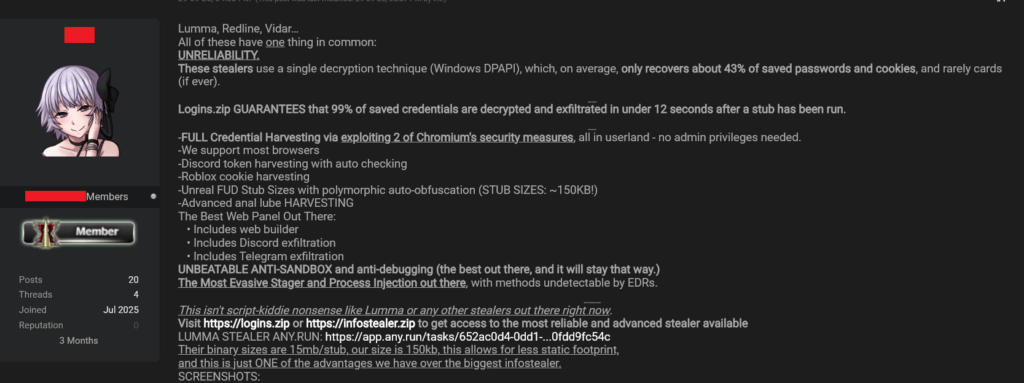
In the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats, Hudson Rock‘s research team has uncovered a potent new Infostealer builder: Logins(.)zip. Marketed as the “go-to infostealer” on underground forums, this web-based tool exploits Chromium browser vulnerabilities to achieve near-total credential extraction – up to 99% of saved logins, cookies, and autofills, in just 12 seconds post-infection.
This marks a significant leap over legacy stealers like Lumma, RedLine, and Vidar, which rely on Windows DPAPI and recover only about 43% of data on average.
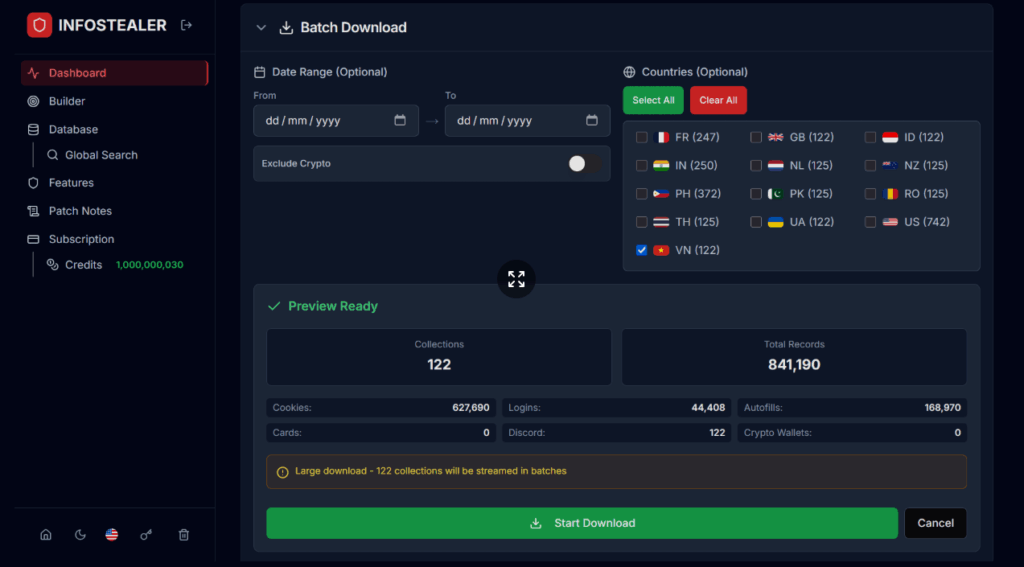
Unlike its predecessors, Logins(.)zip emphasizes evasion, compactness, and reliability, positioning it as a favorite among sophisticated threat actors. Our analysis reveals aggressive promotion via dedicated sites (logins(.)zip and infostealer(.)zip), complete with promotional pricing ending November 10, 2025 ($150/month subscription). Early indicators suggest rapid adoption, with dashboard previews showing data collections from thousands of global infections.

The Threat:Core Capabilities and Evasion Tactics
Logins(.)zip operates as a browser-based builder, allowing operators to generate custom malware stubs without technical expertise. Once deployed, the stub which is clocking in at a mere ~150KB employs polymorphic auto-obfuscation to dodge static detection.
Key features include:
- Full Credential Harvesting: Bypasses User Account Control (UAC) and combines DPAPI with direct exploitation of two undisclosed Chromium security flaws, all in userland for stealth and compatibility. No admin privileges required.
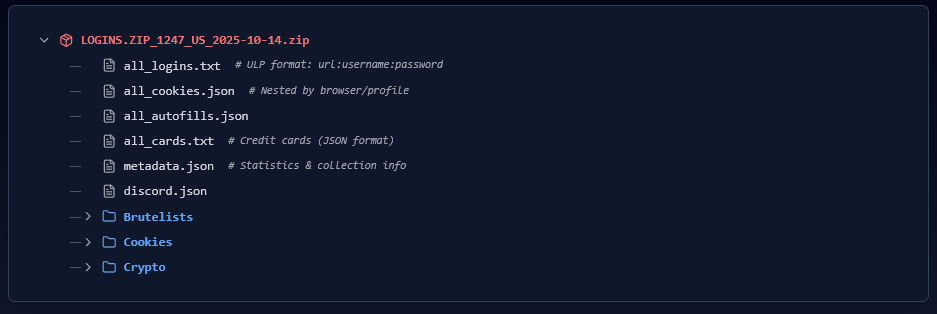
- Broad Target Coverage: Supports Chrome, Brave, Edge, Firefox, Opera, and more. Extracts logins (URL:username:password format), cookies (nested by browser/profile), autofills, and even credit cards (JSON format).
- Specialized Modules: Discord token harvesting with auto-verification, Roblox cookie extraction, and emerging crypto wallet support (daily auto-updates incoming). Metadata JSON provides collection stats for triage.
- Exfiltration and Persistence: Seamless integration with Discord or Telegram bots for data dumps. Advanced anti-sandbox, anti-debugging, and EDR-evasive process injection via direct syscalls with runtime resolution.

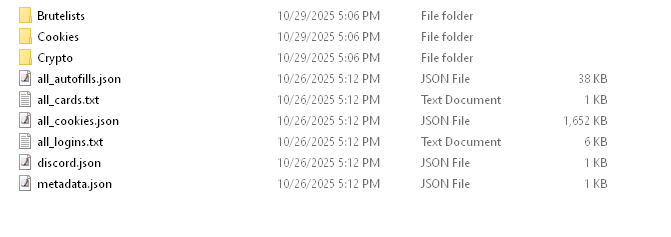
The output zip delivers structured loot: all_logins.txt, all_cookies.json, all_autofills.json, all_cards.txt, metadata.json, discord.json, brutelists, and crypto.json. This efficiency contrasts sharply with bloated rivals like Lumma whose stubs balloon to 15MB, leaving a massive static footprint.
Underground Marketing and Operational Insights
Promoted on dark web forums since at least October 2025, Logins(.)zip is pitched as “real malware” for serious operators, deriding competitors as “script-kiddie nonsense.” A representative thread boasts unbeatable anti-analysis (“the best out there, and it will stay that way”) and links to Any.Run samples of Lumma for side-by-side comparison.
Verification Methods
In order to verify the claims by the vendor behind Logins(.)zip, Hudson Rock’s team did the following:
- Downloaded sample logs from the vendor, the logs indeed show unique structure that we were unable to match to previously seen stealer families
2. Compared the credentials data to existing Infostealer infections, finding never seen before infections
3. In credentials data where existing previous infections where found, our team detected significantly more credentials by the new vendor, speaking to their ability to exfiltrate credentials at a higher rate than other stealer families (147 creds in the new Infostealer vs 99 creds in other ones, in computers infected at a similar time period)
4. Signing into the Infostealer platform in order to verify active development and operationality
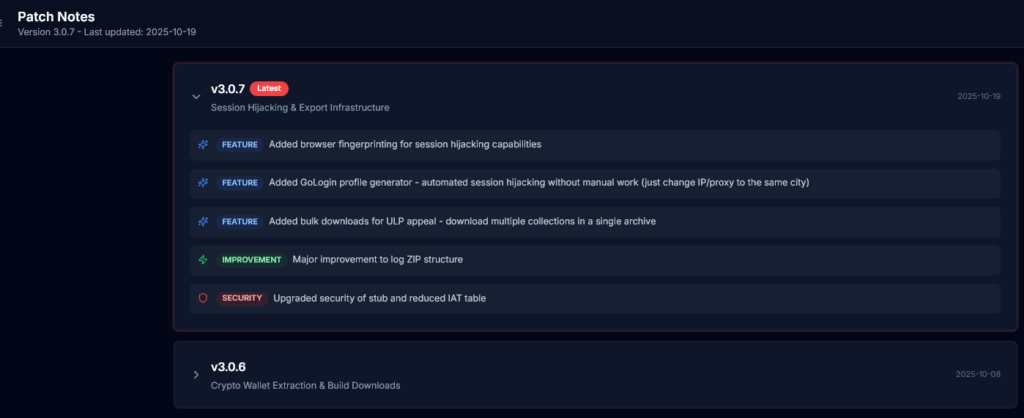
5. When asked about the 0days, login(.)zip said the following:
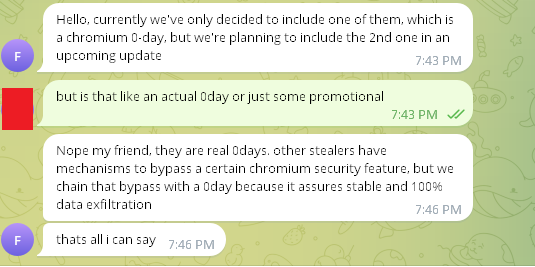
Implications: From Infection to Enterprise Breach
This builder’s speed and stealth amplify its danger. A single compromised endpoint can yield session hijacks on high-security platforms like Jira, enabling zero-touch account takeovers. We’ve observed similar stealers in chains fueling ransomware: In September 2025, a RedLine infection at Collins Aerospace exposed credentials that enabled a separate breach, exfiltrating 1.5M passenger records.
Logins(.)zip’s Chromium focus targets 70%+ of global browsing, with crypto and Discord modules appealing to financially motivated actors. Early forum chatter hints at ties to XMR-only payments, underscoring its appeal in monetized cybercrime ecosystems.
Key Takeaways and Defensive Recommendations
- Prioritize Browser Hardening: Enforce MFA everywhere, rotate credentials quarterly, and monitor for anomalous Chromium processes. Tools like Hudson Rock’s free stealer checker can scan for infections proactively.
- Endpoint Vigilance: Deploy EDR with behavioral analytics tuned for syscalls and userland injections. Compact stubs like these evade signature-based AV – focus on runtime resolution anomalies.
- Intelligence-Led Response: Legacy infections linger; audit for 2022-era stealers that could chain into today’s threats.
To learn more about how Hudson Rock protects companies from imminent intrusions caused by info-stealer infections of employees, partners, and users, as well as how we enrich existing cybersecurity solutions with our cybercrime intelligence API, please schedule a call with us, here: https://www.hudsonrock.com/schedule-demo
We also provide access to various free cybercrime intelligence tools that you can find here: www.hudsonrock.com/free-tools
Thanks for reading, Rock Hudson Rock!
Follow us on LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/hudson-rock
Follow us on Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/RockHudsonRock